6.s081 lab1 util
lab1
选择分支
git checkout util
Boot xv6
环境参考 lab0
sleep
为shell 添加一个可执行的 sleep 程序
在 xv6-labs-2020/usr 添加一个 sleep.c 的文件,作为 sleep 工具代码(用户态)
然后使用 user/user.h 的系统调用来执行 sleep 操作
#include "kernel/types.h"
#include "kernel/stat.h"
#include "user/user.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if (argc != 2)
{
fprintf(0, "usage: sleep <number>\n");
exit(1);
}
int number = atoi(argv[1]);
sleep(number);
exit(0);
}
最后要 exit(0); 不能 return
在 Makefile 添加
UPROGS=\
$U/_cat\
$U/_echo\
$U/_forktest\
$U/_grep\
$U/_init\
$U/_kill\
$U/_ln\
$U/_ls\
$U/_mkdir\
$U/_rm\
$U/_sh\
$U/_stressfs\
$U/_usertests\
$U/_grind\
$U/_wc\
$U/_zombie\
$U/_sleep\
pingpong
为shell 添加一个可执行的 pingpong 程序
父进程 通过管道发送 ping
子进程通过管道收到ping之后 给父进程发送 pong
管道是单向的,为了实现父子进程双边通信,需要使用两个管道
#include "user/user.h"
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int cp[2];
int fp[2];
pipe(cp);
pipe(fp);
int pid = fork();
if (pid==0)
{
close(fp[1]);
char ping[20];
read(fp[0],ping,20);
printf("%d: %s\n",getpid(),ping);
close(cp[0]);
char pong[20]="received pong";
write(cp[1],pong,20);
int status;
wait(&status);
}else{
close(fp[0]);
char ping[20]="received ping";
write(fp[1],ping,20);
close(cp[1]);
char pong[20];
read(cp[0],pong,20);
printf("%d: %s\n", getpid(),pong);
}
exit(0);
//return 0;
}
primes
递归筛选素数,findPrimes(int *array, int len) ,为递归方法,参数是一个数组和长度。
findPrimes 有一个父进程和子进程执行任务。
主进程->打印最小的数,过滤,用管道给子进程发送 新数组
子进程->收到新数组 递归调用 findPrimes()
#include "user/user.h"
#define NUMS 34
void findPrimes(int *array, int len);
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int* array = (int*)malloc(NUMS * sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < NUMS + 2; i++)
{
array[i]=i+2;
}
findPrimes(array,NUMS);
wait(0);
free(array);
exit(0);
}
void findPrimes(int *array, int len){
if (len == 0){
exit(0);
//return;
}
if (len == 1 ){
printf("prime %d\n",array[0]);
exit(0);
}
int p[2];
pipe(p);
int pid = fork();
if (pid == 0)
{
close(p[1]);
// 2.1读取数组长度
int curLen = 0;
read(p[0], &curLen, sizeof(int));
//2.2读取管道array
int* curArray = (int*)malloc(curLen * sizeof(int));
if (curArray==0)
{
printf("error curArray malloc\n");
}
if (read(p[0],curArray,curLen * sizeof(int)) != curLen * sizeof(int)) {
printf("error read array\n");
exit(-1);
}
close(p[0]); // 关闭读端
findPrimes(curArray,curLen);
free(curArray);
exit(0);
}else{
close(p[0]);
int min = array[0];
printf("prime %d\n",min);
int nextLen = 0;
int* newArray = (int*)malloc(len * sizeof(int));
if (newArray == 0) {
printf("error newArray malloc\n");
exit(-1);
}
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
if (array[i] % min != 0) {
newArray[nextLen] = array[i];
nextLen++;
}
}
if (nextLen!=0)
{
//1.1管道发送array长度
if (write(p[1], &nextLen, sizeof(int)) != sizeof(int)) {
printf("error write length\n");
exit(-1);
}
//1.2管道发送array
if (write(p[1], newArray, nextLen * sizeof(int)) != nextLen * sizeof(int)) {
printf("error write array\n");
exit(-1);
}
}
close(p[1]);
//等待子进程
wait(0);
free(newArray);
}
}
find
参考 ls.c 代码,ls是查询当前目录的所有文件
find.c 只需要在ls的基础上,找到输入的文件,如果是目录递归调用find
#include "kernel/types.h"
#include "kernel/stat.h"
#include "user/user.h"
#include "kernel/fs.h"
char* fmtname(char *path)
{
static char buf[DIRSIZ+1];
char *p;
// Find first character after last slash.
for(p=path+strlen(path); p >= path && *p != '/'; p--)
;
p++;
// Return blank-padded name.
if(strlen(p) >= DIRSIZ)
return p;
memmove(buf, p, strlen(p));
memset(buf+strlen(p), ' ', DIRSIZ-strlen(p));
return buf;
}
//findName可能是目录名 或 文件名
void findFile(char *findName,char *path){
char buf[512], *p;
int fd;
struct dirent de;
struct stat st;
if((fd = open(path, 0)) < 0){
fprintf(2, "ls: cannot open %s\n", path);
return;
}
if(fstat(fd, &st) < 0){
fprintf(2, "ls: cannot stat %s\n", path);
close(fd);
return;
}
switch(st.type){
//输入的path是文件直接打印出来
case T_FILE:
printf("%s %d %d %l\n", fmtname(path), st.type, st.ino, st.size);
break;
case T_DIR:
if(strlen(path) + 1 + DIRSIZ + 1 > sizeof buf){
printf("ls: path too long\n");
break;
}
//path 复制到 buf
strcpy(buf, path);
p = buf+strlen(buf);
//buf 最后加一个/ -> path/
*p++ = '/';
//读目录下面所有文件
while(read(fd, &de, sizeof(de)) == sizeof(de)){
if(de.inum == 0)
continue;
// 给 path/ 后面加上这个文件- > path/filename
memmove(p, de.name, DIRSIZ);
p[DIRSIZ] = 0;
if(stat(buf, &st) < 0){
printf("ls: cannot stat %s\n", buf);
continue;
}
//buf 是 path/filename
//只取最后的filename
char *tmpfilename = buf;
for (char *curP = buf; *curP != '\0'; curP++) {
if (*curP == '/') {
tmpfilename = curP + 1;
}
}
//如果buf path/filename 是目录那么递归
if (st.type==T_DIR){
if (strcmp(tmpfilename,".")==0 || strcmp(tmpfilename,"..")==0)
{
continue;
}
//目录名比较
if (strcmp(tmpfilename, findName)==0){
//printf("%s %d %d %d\n",buf , st.type, st.ino, st.size);
printf("%s\n",buf);
}
//递归
findFile(findName,buf);
}else if (st.type==T_FILE){
//文件名比较
if (strcmp(tmpfilename, findName)==0){
//printf("%s %d %d %d\n",buf , st.type, st.ino, st.size);
printf("%s\n",buf);
}
}
}
break;
}
close(fd);
return;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if(argc < 3){
printf("miss parameters\n");
exit(0);
}
char *findName = argv[2];
char *findPath = argv[1];
findFile(findName,findPath);
exit(0);
}
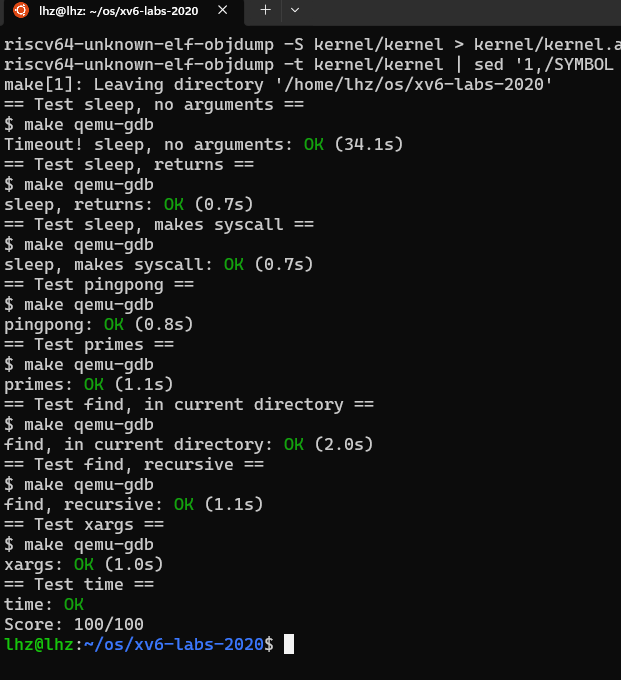
实验结果